Product Design (GCSE)
Subject Vision
GCSE DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY
St George's provides a progressive curriculum that is adventurous and challenging, leading to resilience, curiosity and independence.
The GCSE Curriculum aims to provide an inspiring, rigorous and practical approach to learning in order to develop all learners’ skill, creativity and imagination. Learners will design, make, think critically, learn crucial life skills and become digitally literate. They will develop a broad range of subject knowledge whilst also demonstrating their understanding through designing, analysing and evaluating in a range of contexts
Adventurous – The curriculum enables pupils to be adventurous by taking them out of their comfort zones and becoming innovative, inventive and productive learners through working with materials and creating products, students come to appreciate and respect the complex planning process behind these items.
Challenging – Pupils gain a foundation in fundamental technical concepts, including material selection, manufacturing processes, and design considerations. Through this pupil learn to identify problems, develop potential solutions, and evaluate their effectiveness
Students are encouraged to use their creativity and imagination to solve problems, considering user needs and preference
Resilience – The curriculum encourages pupils to acquire a broad range of subject knowledge whilst learning how to take risks and becoming a resourceful, innovative, enterprising, and capable citizen in an increasingly technological world.
Curiosity - The curriculum delves into more specific areas like materials (metals, polymers, etc.), electronic and mechanical systems, and surface treatments.
Independence – Pupils will learn to: use creativity and imagination to design and make products that solve real and relevant problems including those encountered in their everyday lives.
Community - Pupils have the opportunity to consider the relationships between the society we live in and the impact of their designs considering life cycle, production values and further ethical quandaries equipping them to be the new generation of ethical thinkers and consumers saving our planet. As a result pupils will become the future engineers helping to find solutions to real life problems.
Level 2 Subject Information
SUBJECT INFORMATION GCSE PRODUCT DESIGN
GCSE Product Design, following the AQA specification, focuses on developing students' ability to design and make solutions to real-world problems. It combines theoretical knowledge of materials, manufacturing processes, and design principles with practical skills in creating prototypes. The course emphasizes iterative design, where students investigate, design, make, and evaluate their work, refining their designs based on feedback and testing. A significant portion of the course is dedicated to coursework, which involves creating a product based on a chosen design brief
Core Concepts:
- Designing and Making Principles:
Students learn about various design processes, materials, techniques, and equipment. This includes understanding the importance of user needs, aesthetics, function, and cost in design.
- Material Properties:
The course delves into the properties and applications of different materials, including timbers, polymers, paper, and boards. Students learn how to select appropriate materials for specific design challenges.
- Manufacturing Processes:
Students gain knowledge of various manufacturing techniques and processes, including specialist techniques.
- Iterative Design Process:
This involves a cycle of investigating, designing, making, and evaluating, with ongoing refinement of the product based on feedback and testing.
- Design Communication:
Students learn to effectively communicate their design ideas through various methods, including sketching, technical drawings, and 3D modelling.
- Environmental and Social Impact:
The course encourages students to consider the environmental and social consequences of their design choices.
Assessment:
- Written Exam (50%):
The exam assesses knowledge of core and specialist technical principles, as well as designing and making principles.
- Non-Examined Assessment (NEA) – Coursework (50%):
Students undertake a design and make project, demonstrating their ability to apply the design process and practical skill
Revision
- Revise AQA GCSE (9-1) Design and Technology Revision workbook
- Revision Document
- AQA GCSE Design & Technology | Topic-Based Questions
- GCSE Design and Technology - AQA - BBC Bitesize
Job Opportunities and Careers
Careers in Design and Technology
Design and technology careers offer a diverse range of opportunities combining creativity with technical skills. Popular options include graphic design, user experience (UX) design, web development, software development, and various engineering roles like mechanical, civil, and electrical engineering. Other design-related roles include interior design, product design, and industrial design, while technology-focused roles include game development, animation, and sound engineering.
Examples of Design and Technology Careers:
- Graphic Designer: Creates visual imagery, logos, and layouts for various media.
- User Experience (UX) Designer: Focuses on the user's interaction and experience with a product or service.
- Web Developer: Builds and maintains websites, often incorporating design elements.
- Software Developer: Creates and develops software applications and systems.
- Mechanical Engineer: Designs and develops machines, tools, and systems.
- Civil Engineer: Designs and builds infrastructure like roads, bridges, and buildings.
- Electrical Engineer: Designs and develops electrical systems and components.
- Interior Designer: Plans and designs interior spaces in homes, offices, and other buildings.
- Product Designer: Develops new products, focusing on functionality, usability, and aesthetics.
- Industrial Designer: Designs manufactured products, focusing on aesthetics, ergonomics, and usability.
- Game Designer: Creates and develops video games, combining art, storytelling, and programming.
- Animation: Creates animated visuals for films, television, video games, and other media
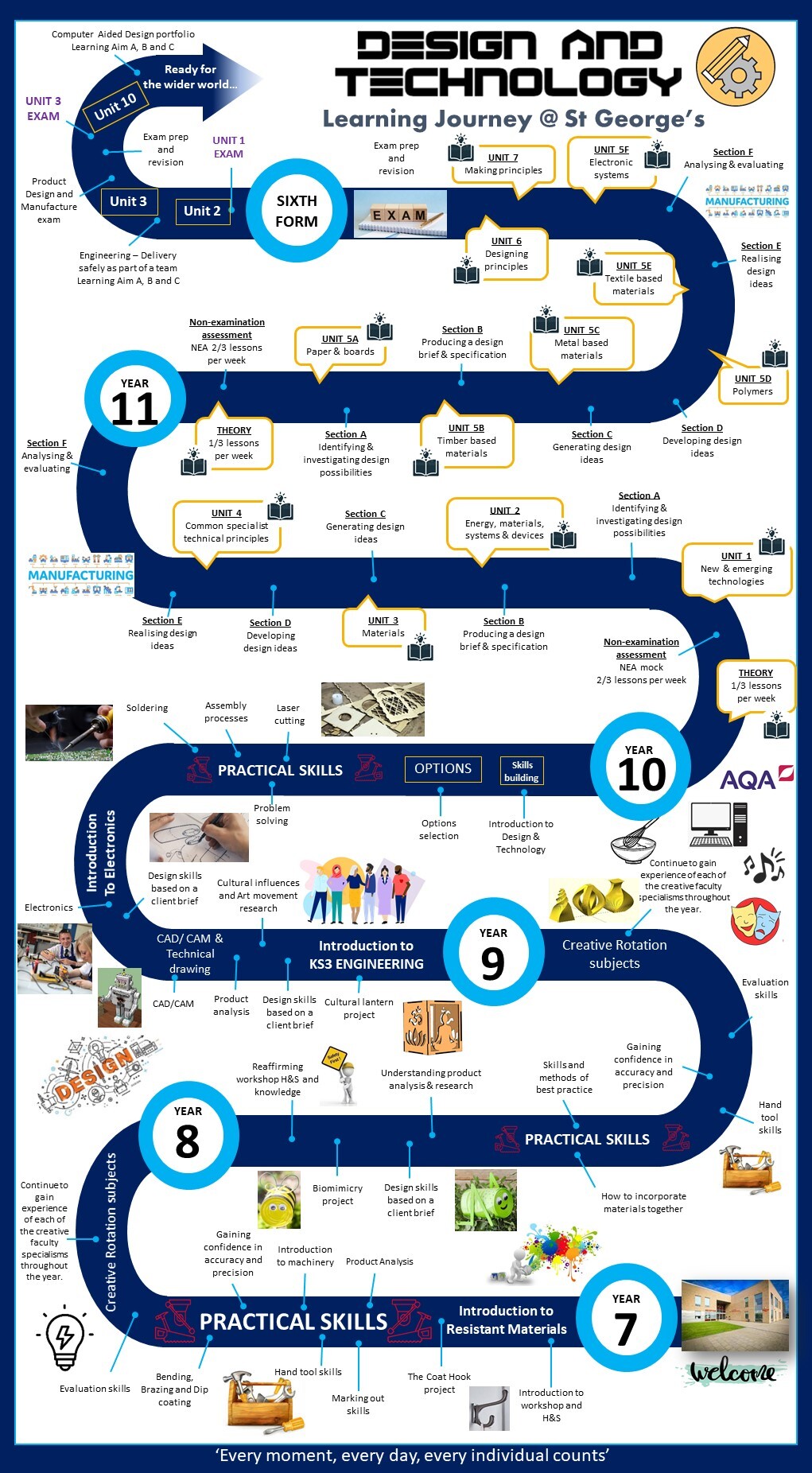
Learning Journey